Sunday, July 5, 2009
Extra qn. answers....
Extra qn....
 The figure shows a miner's safety lamp invented by Sir Humphry Davy. How does the copper gauze act as a safety device to prevent explotions if a flammable gas such as methane is present in the mine? (Hint: Copper is a good conductor of heat. Methane will burn only if the surroundings reach its ignition temperature.)
The figure shows a miner's safety lamp invented by Sir Humphry Davy. How does the copper gauze act as a safety device to prevent explotions if a flammable gas such as methane is present in the mine? (Hint: Copper is a good conductor of heat. Methane will burn only if the surroundings reach its ignition temperature.)Sunday, June 28, 2009
Ans... for the Stuctured Qns....
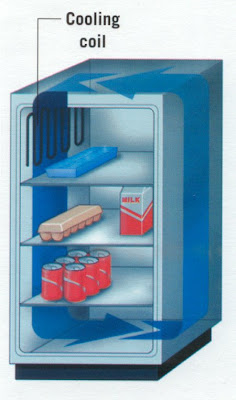
(b) As hotter air from outside moves in, it will quickly rose up, to the freezer compartment being less dense than the cold air inside the refrigerator due to convection current. Thus, the hot air will not have enough time to warm up the contents below the freezer compartment.
(c) The cooling fin of the refrigerator is painted black because black is a better emitter of heat and it radiates heat readily.
2. (a) It is because polished surfaces are bad emitter of heat energy and thus it will prevent heat loss from the kettle to the surroundings.
(b) This is because of convection current. As hot water rises, cold water will sink to take its place and thus it is heated up by the heating element at the bottom.
(c) This is because plastic are a bad conductor, thus it prevents the user from getting scalded.
3. (a)(i) Radiation
(ii) Conduction
(b)(i) d.Black-painted copper
(ii) This is because copper is a good conductor of heat and therefore will quickly transfer the heat to the water. Secondly, black surfaces is a better absorbers of heat rather than white, polished surfaces.
4. (a) When birds fluff up their wings, it is trapping air, and as air is a bad conductor of heat, the heat from its body would not be lost to the surroundings cold air.
(b) This is due to the over-exposure of radiation from the sun, and the radiation will make the skin cells act abnormally.
Structured Qns...
(b) When the refrigerator door is opened for a short time, the cold air inside is replaced by the warmer air outside. Why does this exchange of air have little effect on the temperature of the contents in the part of the refrigerator below the freezer compartment ?
(c) Explain why the cooling fins at the back of the refrigerator is black.
2. (a) Explain why a household electric kettle has a polished surface.
(b) What is the reason for placing the heating element at the bottom of the kettle?
(c) Most kettles have plastic handles. Why?
3. A solar panel is used to heat water.
(a) State the name of the process by which energy is transferred
(i) from the Sun to the outside of the pipe in the solar panel.
(ii) from the outside of the pipe to the water inside it.
(b) (i) Which of the following materials would be the most suitable for the pipe that contains the water
a. black plastic
b. white plastic
c. glass
d. black-painted copper
e. polished steel
(ii) Give two reasons for your choice of material.
4. Explain the following observations.
(a) Birds usually fluff up their feathers during cold weather
(b) Excessive sunbathing can cause skin cancer
Saturday, June 27, 2009
Answers for MCQs!!!
1. C
2. D
3. A
4. A
5. B
Part 2:
6. A
7. C
8. B
9. B
10. C
Part 3:
11. B
12. C
13. A
14. D
15. B
MCQss!!!! Part 3
 12. Identify the procesess of thermal energy transfer.
12. Identify the procesess of thermal energy transfer.  13. A person sits in front of a warm fire. What is/are the main process(es) of thermal energy transfer?
13. A person sits in front of a warm fire. What is/are the main process(es) of thermal energy transfer? A Radiation only
B Convection and radiation
C Conduction and radiation
D Conduction, convection and radiation
14. An experiment is carried out as shown.
An experiment is carried out as shown.
Why does the ice take a long time to melt, even when the water at the top of the test-tube
is boiling?
A Ice is a poor radiator of heat.
B Convection cannot occur in water.
C The metal gauze prevents heat from melting the ice.
D Water is a poor conductor of heat.
15. Two cars were painted, one was in black, the other white. The cars were left under the sun to dry. The black paint dried more quickly than the white paint. Which property of black paint makes it dry more quickly?
A It is a better conductor of heat.
B It is a better absorber of heat.
C It is a better insulator of heat.
D It is a better reflector of heat.
MCQss!!! Part 2
 7. In a vacuum flask, which methods of heat transfer are prevented by the vacuum?
7. In a vacuum flask, which methods of heat transfer are prevented by the vacuum?8. A teacher has a large tank of water in which he wants to set up a convection current.
A cooling at X
C heating atY
 At which temperatures are the blocks in thermal equilibrium?
At which temperatures are the blocks in thermal equilibrium? 10. Four beakers containing the same amount of water at the same temperature are placed on hot metal plates. The lower surfaces of the metal plates are kept at the same temperature.
10. Four beakers containing the same amount of water at the same temperature are placed on hot metal plates. The lower surfaces of the metal plates are kept at the same temperature. The plates are all the same size but are made from four different metals
 The time taken to produce stated temperature rises of the water are given below.
The time taken to produce stated temperature rises of the water are given below. 
MCQ!!! Part1

D radiation and convection
 How does fibre prevent heat passing easily through the ceiling?
How does fibre prevent heat passing easily through the ceiling? A Fibre allows air to pass through easily.
B Fibre is tightly packed
C Fibre is warm.
D Fibre traps air.
3. Which material is the best absorber of infra-red radiation?
A dark animal fur
B shiny metal
C window glass
D white paper
4. The diagram shows a metal saucepan containing water and
placed on a hot plate. After some time, the air at point X also
becomes hot.
 What are the main ways by which heat travels from the hot
What are the main ways by which heat travels from the hotplate through the base of the metal saucepan' through the
water and through the air to Point X?
 5. Density changes are responsible for which methods of thermal energy transfer?
5. Density changes are responsible for which methods of thermal energy transfer?A conduction only
B convection only
C radiation only
D conduction, convection and radiation
Wednesday, June 24, 2009
Thermal conductivity of substances
Substance | Thermal Conductivity | Substance | Thermal Conductivity |
Syrofoam | 0.010 | Glass | 0.80 |
Air | 0.026 | Concrete | 1.1 |
Wool | 0.040 | Iron | 79 |
Wood | 0.15 | Aluminum | 240 |
Body fat | 0.20 | Silver | 420 |
Water | 0.60 | Diamond | 2450 |
Factors affecting rate of infrared radiation
Thursday, June 18, 2009
Wednesday, June 17, 2009
Sunday, June 14, 2009
Absorption and Emission of infrared radiation
bad emitter is also a bad absorber (of radiant heat)
 Good emitter and absorber:
Good emitter and absorber:Dull, black surfaces
Bad emitter and absorber:
Saturday, June 13, 2009
Radiation
Examples of convection
 Water has a larger heat capacity than land, and subsequently holds heat better. It therefore takes longer to change its temperature, either upward or downward. Thus, during the day the air above the water will be cooler than that over the land. This creates a low pressure area over the land, relative to the high pressure area over the water, and subsequently one finds breezes blowing from the water to the land. On the other hand, during the night water cools off more slowly than the land, and the air above the water is slightly warmer than over the land. This creates a low pressure area over the water relative to the high pressure area over the land, and breezes will blow from the land to the water.
Water has a larger heat capacity than land, and subsequently holds heat better. It therefore takes longer to change its temperature, either upward or downward. Thus, during the day the air above the water will be cooler than that over the land. This creates a low pressure area over the land, relative to the high pressure area over the water, and subsequently one finds breezes blowing from the water to the land. On the other hand, during the night water cools off more slowly than the land, and the air above the water is slightly warmer than over the land. This creates a low pressure area over the water relative to the high pressure area over the land, and breezes will blow from the land to the water.  Thx:http://theory.uwinnipeg.ca/mod_tech/node76.html
Thx:http://theory.uwinnipeg.ca/mod_tech/node76.html
Convection
 What is convection?
What is convection?Conduction in Liquids and Gases
Conduction in metals and non-metals
 What is atomic or molecular vibrations?
What is atomic or molecular vibrations?When thermal energy is supplied to one end of the rod, the particles (atoms or molecules) at the hot end vibrate vigorously. These particles will collide with neighbouring particles, making them vibrate as well. Thus, the kinetic energy of the vibrating particles at the hot end is transferred to the neighbouring particles.
This process is slow.
When the coppper rod is heated, the free electrons in the copper gain kinetic energy and move faster as a result. These fast-moving electrons then diffuse or spread into the cooler parts of the metal. In the process, they collide with the atoms in the cooler parts of the metal and transfer their kinetic energies to them.
This is a much faster mechanism of thermal energy transfer.
This explains why the conduction in metals is faster than in non-metals. Thus metal is a good conductor of heat and non-metals is a poor conductor of heat.
metals, eg. copper, silver, steel and iron
non-metals, eg. glass, plastic, wood, brick, wool
Conduction
Conduction is the process of thermal energy transfer without any flow of the material medium.
It is also the transfer of thermal energy between neighboring molecules in a substance due to a temperature gradient.
Conduction is most effective in solids, but it can happen in liquids and gases.
 eg. a spoon in a cup of hot soup becomes warmer because the heat from the soup is conducted along the spoon.
eg. a spoon in a cup of hot soup becomes warmer because the heat from the soup is conducted along the spoon.Fun fact:
Have you ever noticed that metals tend to feel cold? Actually, they are not colder. They only feel colder because they conduct heat away from your hand. You perceive the heat that is leaving your hand as cold.
Thermal energy transfer
Transfer of thermal energy
Thermal energy is only transferred when there is a difference in temperature.
Thermal energy always flows from a region of higher temperature to a region of lower temperature (temperature gradient) to equalize temperature differences (reach equilibrium).
When thermal equilibrium is reached, there is no net flow of thermal energy.